The Evolution of Calling from Your Computer: From VoIP Pioneers to the AI-Powered, Immersive Future
Executive Summary: The ability to place a voice call from a computer has evolved from a 1973 ARPANET experiment into a $50 billion industry that serves billions daily. This comprehensive analysis traces the journey through three transformative eras—from VoIP's disruption of telecom monopolies, through WebRTC's democratization of real-time communication, to today's AI-powered platforms racing toward holographic futures.
Key Insights:
- ✓ Skype's rise and fall: From 300M users to shutdown in 2025
- ✓ WebRTC powers 95% of browser-based calling globally
- ✓ 79% of workers now remote/hybrid, driving platform wars
- ✓ AI assistants adopted by 65% of companies in 2025
What You'll Learn:
- ✓ Complete history from ARPANET to modern platforms
- ✓ Head-to-head comparison: Zoom vs Teams vs Meet vs Discord
- ✓ Technical deep-dives: Codecs, encryption, WebRTC
- ✓ Future predictions: AR/VR collaboration & holograms
50 Years of Innovation: Key Milestones
The birth of digital voice: Sound waves transform into data packets on the early ARPANET, marking the dawn of VoIP technology
First VoIP call on ARPANET
VocalTec launches commercial VoIP
Skype revolutionizes P2P calling
WebRTC democratizes browser calling
Pandemic drives video explosion
AI assistants become standard
E2EE and holographic future
Chapter 1: The Genesis of Digital Voice
The concept of transmitting voice over a digital network emerged from decades of foundational research in voice synthesis, packet networking, and data compression. The journey began not with the internet, but with a 1928 invention at Bell Labs.
1928: The Vocoder
Homer Dudley's Voice Coder at Bell Labs demonstrated the fundamental principle of modern codecs: deconstructing and reconstructing human speech. Used in WWII for encrypted Allied communications.
1969: ARPANET Launch
The first operational packet-switching network created the infrastructure needed for VoIP. Unlike circuit-switched phones, packets could travel independently and be reassembled.
1973: First VoIP Transmission
MIT Lincoln Lab successfully transmitted voice data packets over ARPANET using Linear Predictive Coding (LPC), reducing voice data by 10x while maintaining intelligibility.
1974-1976: Real-Time Calls
First two-way VoIP call between Culler-Harrison Inc. and MIT. By 1976, achieved multi-party conference calls over the network. Core VoIP technology was born.
The Pioneers of Commercial VoIP (1990s)

The VoIP explosion: Services like Skype connected the world with free calls, breaking telecom monopolies
For two decades, packet voice remained confined to research labs and military networks. The catalyst for commercialization was the convergence of personal computers and the public internet in the early 1990s.
John Walker (Autodesk founder) released the first widely available software VoIP phone into public domain, proving consumer viability.
Israeli company launches Internet Phone, the first commercial VoIP product. Required 486 processor, 8MB RAM. Telcos petition Congress to ban it.
ITU develops H.323 protocol. IETF creates SIP (Session Initiation Protocol). Broadband adoption improves call quality dramatically.
No company is more synonymous with internet calling than Skype. Its journey from disruptive startup to global giant to eventual shutdown offers crucial lessons about technology, strategy, and market adaptation.
Disruption Through Innovation
- P2P Architecture: Each user's computer acted as a "supernode," routing calls for others. Minimal infrastructure costs.
- Firewall Traversal: Clever NAT traversal eliminated complex configuration, working "magically" behind corporate firewalls.
- Extreme Stealthiness: Deliberately hard to detect/block, growing to millions before telcos could respond.
- Network Effect: 300M active users by 2013, became the verb for video calling.
Seeds of Decline
- 2011 Microsoft Acquisition: $8.5B purchase led to corporate integration over user innovation.
- Architecture Abandonment: Moved from P2P to centralized servers, degrading quality and reliability.
- Mobile Failure: Clunky apps lost to WhatsApp, Viber built mobile-first.
- Internal Cannibalization: Microsoft Teams launched 2017, became priority. Skype shuts down May 5, 2025.
Chapter 2: The Browser as the Phone - WebRTC Revolution

WebRTC revolution: Browsers become phones with direct peer-to-peer connections, no plugins required
Before WebRTC:
- • Required plugins (Flash, Silverlight, Java)
- • Security vulnerabilities from third-party software
- • Poor user experience with downloads/updates
- • Developer nightmare with platform compatibility
- • No native browser support for real-time media
After WebRTC (2011-Present):
- • Plugin-free, native browser support
- • Open-source, royalty-free standard
- • Simple JavaScript APIs
- • 95%+ global browser compatibility
- • Mandatory codec support ensures interop
The Technical Architecture
getUserMedia API
Gateway to hardware. Captures audio/video from camera and microphone with explicit user permission.
RTCPeerConnection
Heart of WebRTC. Handles peer-to-peer connections, codec negotiation, encryption, and bandwidth management.
RTCDataChannel
Low-latency, bidirectional data exchange for chat, file sharing, and collaborative features.
ICE/STUN/TURN
Sophisticated NAT traversal ensures connections work behind firewalls. STUN discovers public IP, TURN relays when P2P impossible.
Chapter 3: The Catalyst - Remote Work Revolution

The new normal: Remote teams connected through video conferencing platforms, transforming work culture globally
The New Normal: Work Location Distribution 2025
36.2 million Americans (22% of workforce) will be fully remote by end of 2025
- 1. Unclear communication protocols35%
- 2. Too many meetings34%
- 3. Time zone differences32%
- 4. Disconnection from culture28%
- 5. "Always-on" pressure26%
- Email (still dominant)98%
- Company intranets77%
- Microsoft Teams63%
- Video for messaging52%
- AI-powered tools65%
Chapter 4: The Battle for the Desktop - Platform Analysis 2025

The platform wars: Zoom, Teams, Meet, and Discord compete for dominance in the $50 billion communication market
300M+ active users
Video quality & reliability
Limited ecosystem integration
Large meetings, webinars, education
$14.99/user/month Pro
320M+ active users
Deep Microsoft 365 integration
Complex interface
Enterprise, Microsoft shops
$4/user/month (in M365)
100M+ active users
Browser simplicity
Limited advanced features
SMBs, education, quick calls
$6/user/month (Workspace)
200M+ active users
Persistent voice channels
Lacks enterprise features
Communities, gaming, informal teams
Free (Nitro $9.99/month)
Chapter 5: The Unseen Foundation - Codec Evolution
Audio Codec Evolution: From Phone Quality to AI Enhancement
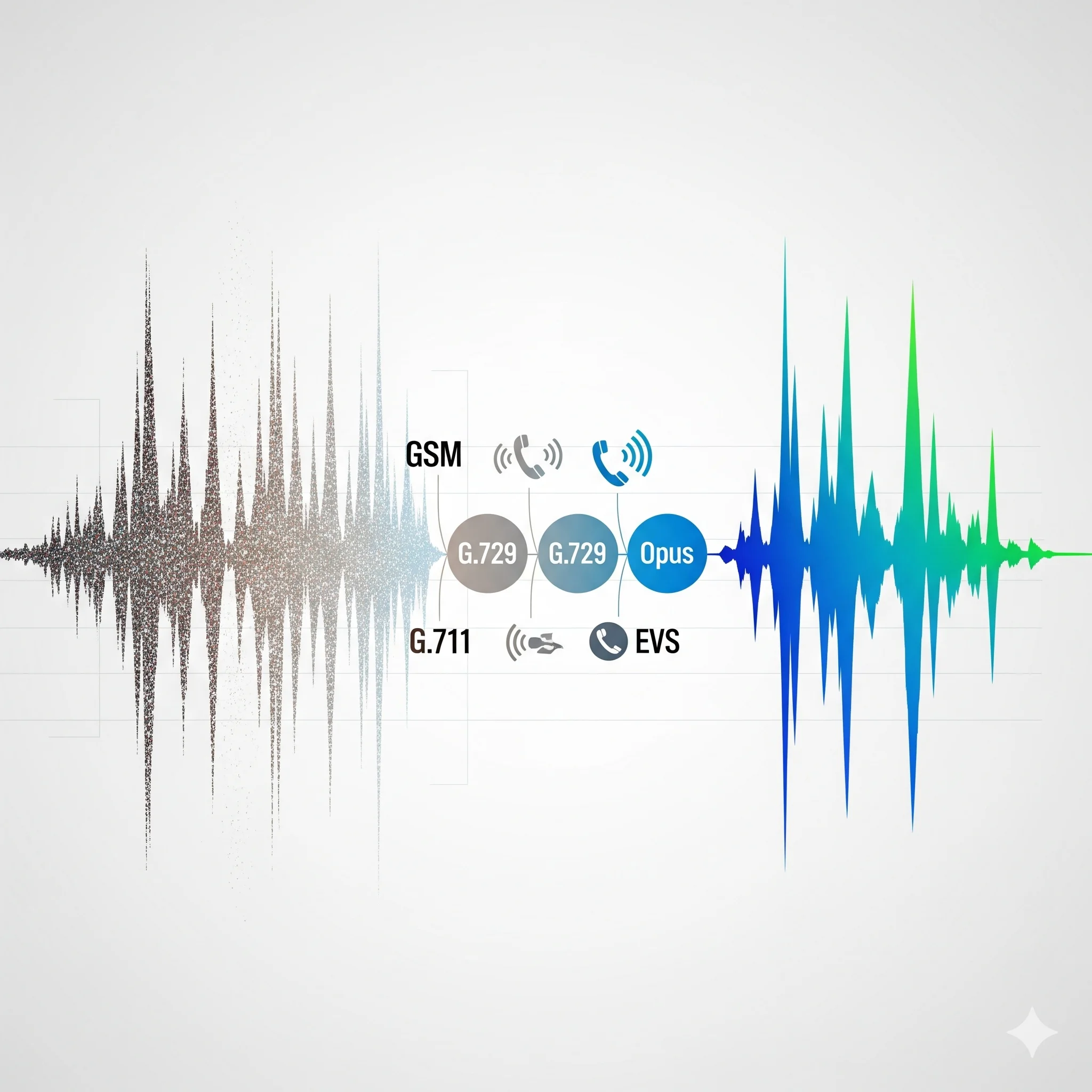

Crystal clear evolution: From 8 kbps compressed audio to AI-enhanced HD voice with noise cancellation
Combines Skype's SILK + Xiph.Org's CELT. Mandatory for WebRTC.
- • Adaptive: 6-510 kbps dynamically
- • Scales: Narrowband to full-band audio
- • Low latency: 5ms to 60ms
- • Handles voice AND music
- • Royalty-free and open-source
Machine learning models trained on vast speech datasets.
- • Google Lyra: 3 kbps with high quality
- • Microsoft Satin: Enhanced clarity
- • Works on extremely poor networks
- • Can reconstruct lost packets
- • Future: Real-time voice translation
Video Codec Wars: Patents vs Open Standards
| Codec | Year | Efficiency | Royalties | Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| H.264/AVC | 2003 | Baseline | Yes | Industry standard, universal support |
| VP8 | 2008 | Similar to H.264 | Free | WebRTC mandatory codec |
| H.265/HEVC | 2013 | 50% better | Complex | 4K streaming, limited browser support |
| VP9 | 2013 | 35% better | Free | YouTube default, good support |
| AV1 | 2018 | 30% better than VP9 | Free | Future standard, growing adoption |
Chapter 6: Securing the Conversation - Privacy & Encryption

Fort Knox for conversations: End-to-end encryption shields your calls from digital threats and surveillance
The Journey to End-to-End Encryption
Discord is making the boldest move in the industry: E2EE by default for ALL voice/video by March 1, 2026.
How DAVE Works
- • Uses RTCRtpScriptTransform API in WebRTC
- • Inserts encryption directly in media pipeline
- • Messaging Layer Security (MLS) for groups
- • Keys only known to participants
- • Discord servers can't decrypt
Strategic Trade-off
- • Voice/Video: Fully E2EE protected
- • Text Chat: NOT encrypted (for moderation)
- • Balances privacy with safety
- • Allows content scanning for violations
- • Industry-leading for consumer platform
- Zoom: No customer content for AI training
- Google: No data for advertising, no attention tracking
- Microsoft: Data within compliance boundary
- Discord: Doesn't sell personal data
- Enable E2EE when available
- Use waiting rooms and passcodes
- Verify meeting links before joining
- Regular security training for teams
Chapter 7: The Intelligent Co-Worker - AI Integration

Your AI co-pilot: Intelligent assistants provide real-time transcription, summaries, and action items
Companies using AI communication tools
Projected labor cost savings by 2026
Reduction in meeting follow-up time
AI Features Transforming Meetings
Live captions with 95%+ accuracy, speaker identification, keyword highlighting
AI-generated meeting notes, key decisions, action items auto-assigned
Late joiners get instant summary without interrupting flow
Search across meetings, emails, docs for unified knowledge
Chapter 8: The Next Frontier - Immersive Communication

Beyond the screen: Holographic telepresence promises face-to-face conversations without physical presence
AR for Remote Assistance
- • First-person view sharing
- • AR annotations on live video
- • 3D model overlays
- • Manufacturing, field service adoption
- • ROI proven, scaling rapidly
VR Meeting Rooms
- • Avatar-based presence
- • Spatial audio environments
- • 3D whiteboarding
- • Training and design focus
- • WebXR browser support
Holographic Telepresence
- • Life-size 3D projections
- • No glasses required
- • Google Project Starline
- • Massive bandwidth needs
- • Consumer: 5-10 years away
Capture Challenge
Requires array of cameras/sensors to capture 3D geometry and texture in real-time. Current: Bulky and expensive.
Bandwidth Requirements
Volumetric video needs 100-1000x more data than 2D. Requires 5G/fiber with <5ms latency. Infrastructure not ready.
Display Technology
True holograms need light field displays. Current "holograms" use Pepper's Ghost illusion. Consumer tech years away.
Appendix: Technical Requirements 2025
WebRTC Browser Support
✓ Full Support (95%+ coverage)
- • Chrome 90+ (Desktop & Mobile)
- • Firefox 85+ (Desktop & Mobile)
- • Safari 14.1+ (Desktop & iOS)
- • Edge 90+ (Chromium-based)
- • Opera 76+
Mandatory Codecs
- Audio: Opus, G.711 (PCMU/PCMA)
- Video: VP8, H.264 (Baseline)
- Future: AV1 adoption growing
Interop 2025 initiative ensuring cross-browser consistency for RTCRtpScriptTransform (E2EE) and advanced features.
The journey of computer-based calling reflects the broader arc of technology: cycles of disruption where open protocols foster innovation, which becomes the foundation for new ecosystems that capture value at higher levels.
The Three Eras
Pioneer Era (1973-2010)
Battle for access. VoIP challenged telecom monopolies. Skype's P2P revolution brought free calling to millions.
Standardization Era (2011-2020)
WebRTC democratized real-time communication. Browser-native calling eliminated friction, commoditized transport layer.
Intelligence Era (2021-Present)
AI transforms meetings into structured data. Platforms compete on ecosystem integration and intelligent automation.
Looking Ahead
The strategic tension between open standards and closed ecosystems will continue. Winners will navigate this balance, making communication more:
Intelligent
AI handles logistics
Context-Aware
Cross-app integration
Present
3D immersive reality
The future path leads from today's 2D screens augmented by AI toward truly immersive 3D presence—where the distinction between physical and virtual conversation finally disappears.
Frequently Asked Questions
The first VoIP transmission occurred in 1973 at MIT Lincoln Lab over ARPANET. The first real-time, two-way VoIP call happened in 1974 between Culler-Harrison Inc. and MIT.
Microsoft is shutting down Skype on May 5, 2025, after cannibalizing it with Microsoft Teams. Key failures included abandoning P2P architecture, poor mobile adaptation, and strategic misalignment after the 2011 acquisition.
WebRTC democratized real-time communication by making it a free, plugin-free browser feature. With 95%+ global support, it eliminated the need for downloads and made voice/video calling accessible to any website.
Zoom consistently ranks highest for video/audio quality and reliability, even on poor networks. This singular focus on call quality is their primary competitive advantage.
True E2EE means only participants can decrypt content—not even the platform provider. Discord will have the most comprehensive E2EE by March 2026, while others offer it selectively.
AI assistants use speech-to-text for transcription, natural language processing for summarization, and machine learning to detect action items. They're solving meeting fatigue and information silos.
Opus is the gold standard for audio (6-510 kbps adaptive). For video, AV1 offers the best compression but H.264 has the widest support. AI codecs like Google Lyra achieve quality at just 3 kbps.
AR collaboration tools are viable now for industrial use. VR meeting rooms will grow through 2027-2030. True holographic telepresence for consumers is likely 5-10 years away due to bandwidth and display challenges.
Related Articles
Navigate the complex legal landscape of call recording across all 50 states.
Read More →Master call flow optimization to reduce abandonment and improve customer satisfaction.
Read More →Coming soon: Smart strategies for managing international business calls efficiently.
Coming Soon